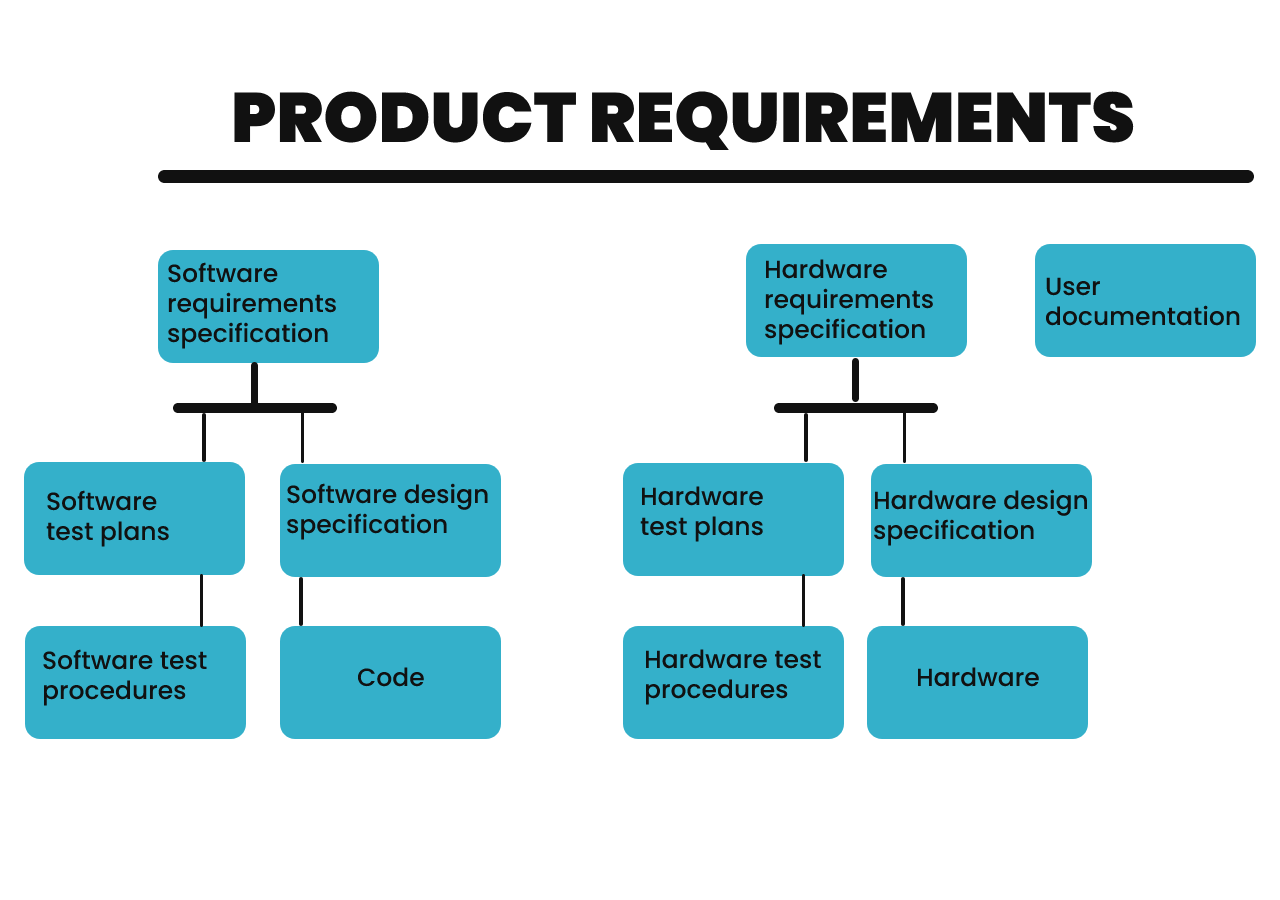
The PRD is one of the most important documents that a project manager must write and update with his team. It defines the value and purpose of a product and should enable the product development team to understand the product’s capabilities, functionality and features in sufficient detail. The document should evolve as the product development iterations progress.
It is also used to provide all members of an organization with the same level of knowledge about how the product works and thus exclude misunderstandings or misinterpretations. Engineers use it to implement the function as needed, sales teams to write documents and sales pitches, and management to have a global view of the project.
PRD versus MRD
Be careful not to confuse the PRD and the MRD (Market Requirement Document), which is written upstream and allows the definition of customer needs, contains functional requirements and serves as a basis for drafting the PRD, whereas the PRD lists the technical and functional specifications of the project. The MRD is the highest level of marketing analysis. It deals with issues such as customer requirements, market, competition and price.
PRD versus Spec
PRD’s redaction
The PRD redaction must follow a top-down approach that starts with the overall vision of the project. It is necessary to question all the actors involved: the technique, the production, the method function, the marketing… In order to formalize the functionalities of the product right from the start, to anticipate the development costs and to supervise the progress of the project. A well-defined PRD also includes details on how the end user will interact with the functionality, and what that functionality will look like. It is a deliverable of the feasibility phase that is intended to be fixed, but modifications can be made throughout the product development process using ECR (Engineering Change Request). The FDP will therefore be versioned during the different phases.
What PRD must contains?
– Goals: explain why you are building this product.
– Characteristics: for each element, you must include at least a description, an objective and a use case. Additional details may be useful or necessary depending on the complexity of the element.
– User flow: Include schematics and mock-ups to help engineers understand the product and how functionality should be implemented.
– System and environment requirements
– Assumptions, Constraints and Dependencies: List what is expected from users, the limitations that must be taken into account for implementation, and the external elements necessary for the final solution to be functional.
Plan (exemple):
1- General information about the project
Goals
Planning
Roles and Responsibilities
2- Overview
Feature Listing
Basic use
User flow
3- Functional specifications (operational requirements)
4- Production, industrialization and quality assurance
Packaging
Calibration and production line testing
Environmental constraints
Factory Supply
Compliance
Product labelling and marking requirements
Industrial process
Il n’existe pas de vérité établie sur le PRD, comment il doit être rédigé et ce qu’il doit contenir. Chacun fait un peu à sa manière et ce que nous vous proposons en une.