
Biomimicry refers to approaches that draw inspiration from nature to innovate and create the conditions for a renewed, sustainable development model. It presents a significant opportunity for the future, emerging rapidly as a cross-sector approach central to the breakthrough innovation strategies of many companies, research centers, and pioneering businesses.
Nature has always been a source of human innovation, but today, biomimetics addresses critical transitional issues:
- conserving energy,
- optimizing local supply chains,
- reducing waste,
- rethinking agriculture,
- embracing circular economies,
- combating global warming,
- creating resilient housing and urban areas,
- integrating growth with biodiversity,
- and fostering open, collaborative systems.

What is the link between technology and biomimicry?
The connection between technology and biomimicry is rooted in how technology often takes inspiration from biological systems to address complex human challenges. Biomimicry involves studying the patterns, systems, processes, and elements of nature to emulate or draw inspiration from them, leading to the design of innovative solutions.
We owe nature many advances!
Some of the tech examples we’re about to share might surprise you if you haven’t heard of them:
➔ In the field of robotics and drones:
- Animal-inspired robots: many robots mimic the movements of animals, such as Boston Dynamics‘ robots, which emulate the agility and balance of dogs and cheetahs.
- Octopus tentacle movement: used to design flexible, highly maneuverable robots for surgery and manufacturing processes.
- Swarm behavior: the collective behavior of ants and bees has inspired the design of small robots that work together for tasks like search and rescue or environmental monitoring.
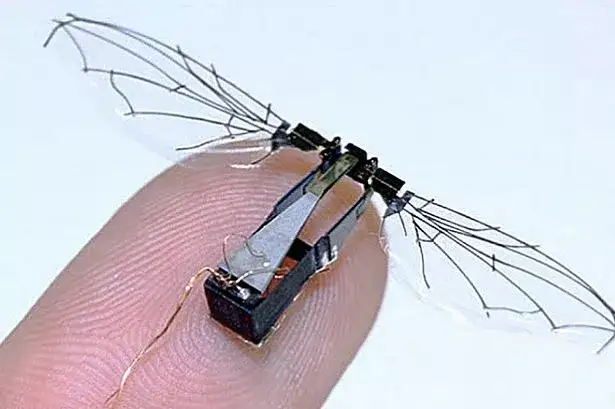
- Bird and insect flight patterns: used to create drones with greater stability, agility, and energy efficiency for surveillance, agriculture, and delivery services.
Remember, the helicopter was invented thanks to the dragonfly!
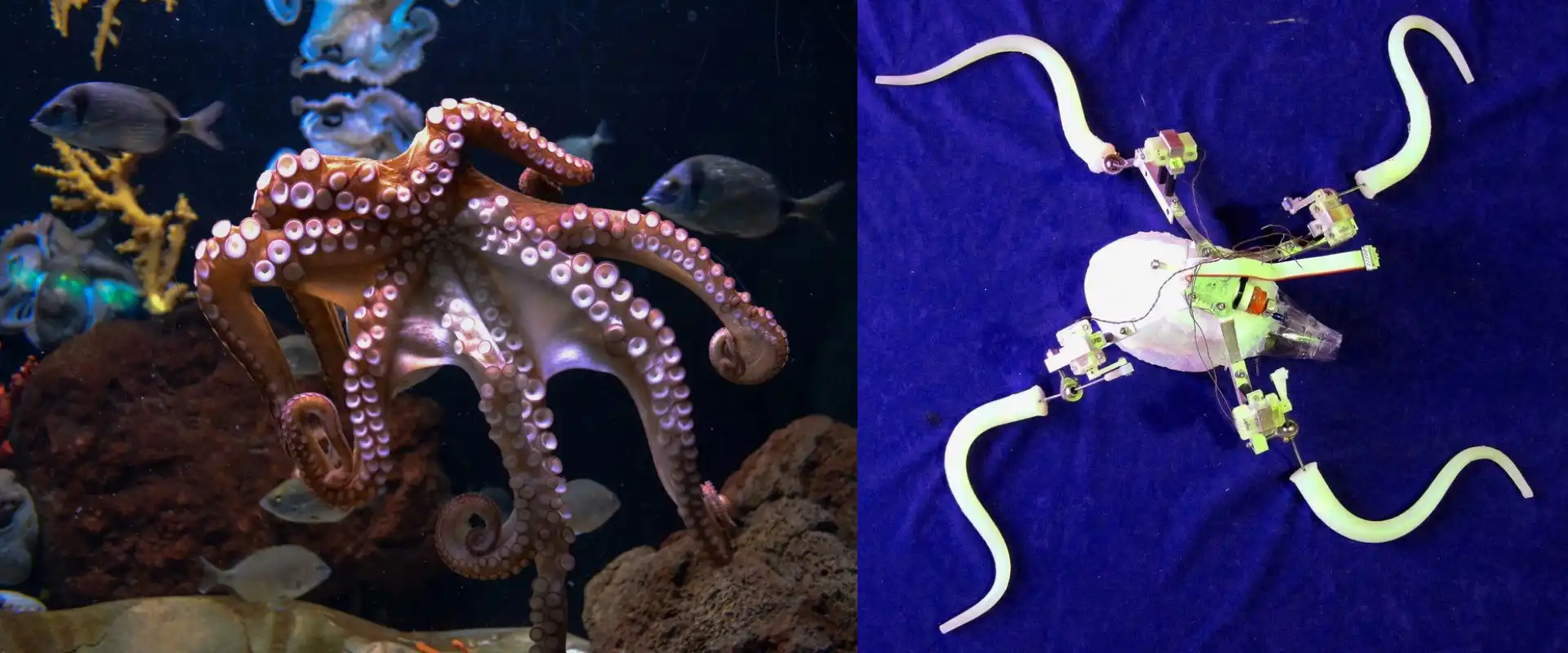

➔ In the medical field, biomimicry has led to innovations such as:
- Biomimetic sensors: these devices mimic the sensitivity of human skin or the olfactory abilities of dogs, and are utilized in medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
- Prosthetic limbs: designed to emulate the natural movement and functionality of biological limbs, these prostheses provide amputees with more effective and comfortable alternatives.
- Development of a surgical polymer: Maria Pereira from TISSIUM explored the adhesive properties of shellfish like barnacles to aid in developing a polymer suitable for surgical use. The primary challenge was creating a substance that could bond wet tissues together. Tissium’s foundational technology involves using a viscous liquid that seals human tissues in a moist environment. This liquid remains localized without spreading and is activated by blue light.
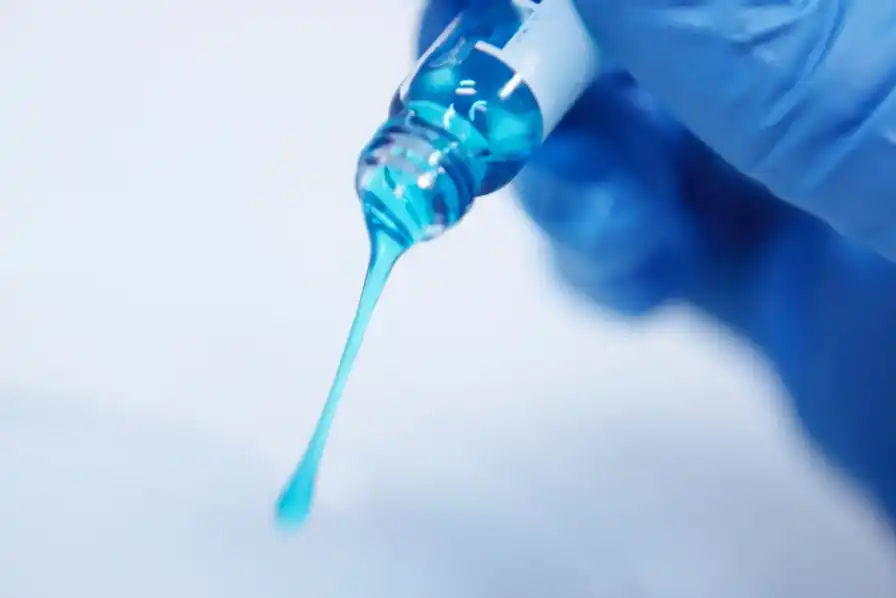
@tissium
➔ In Aerospace and transportation:
- Aerodynamics: the study of bird flight and fish fin structures has shaped the design of more efficient and agile aircraft and underwater vehicles.
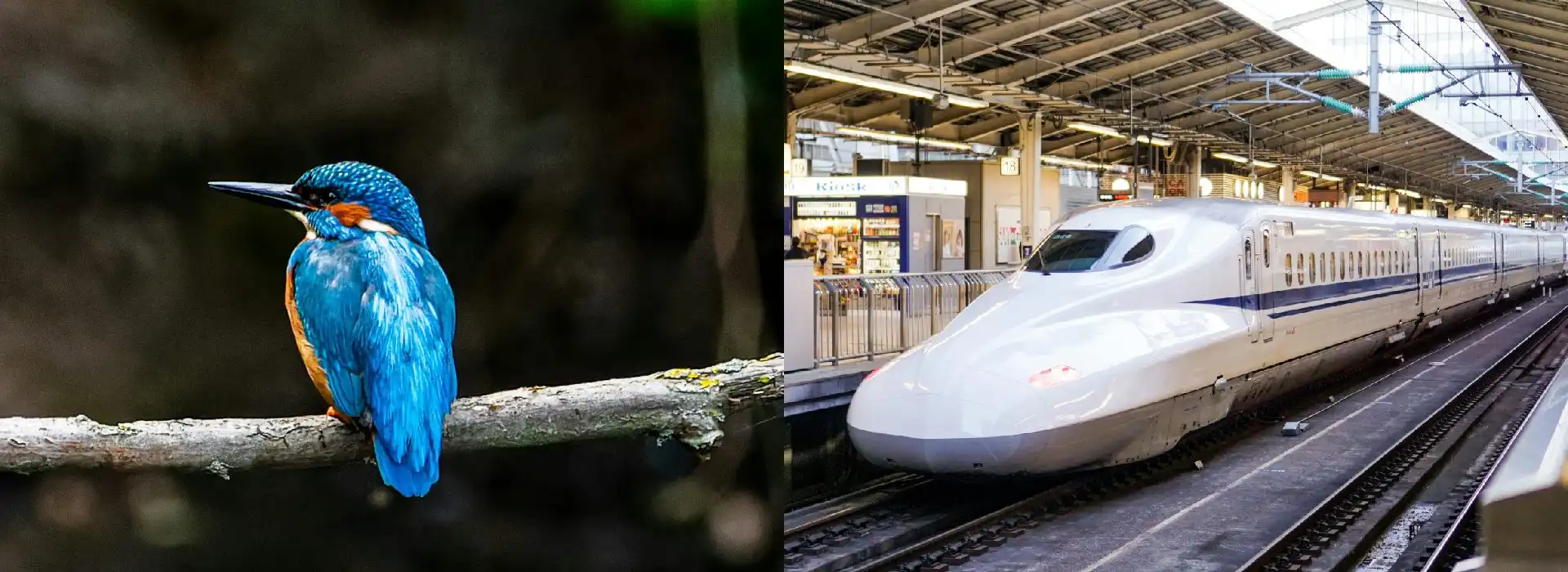
- High-speed trains: the design of the nose on Japan’s Shinkansen high-speed train, inspired by the kingfisher’s beak, reduces noise and enhances speed and efficiency.
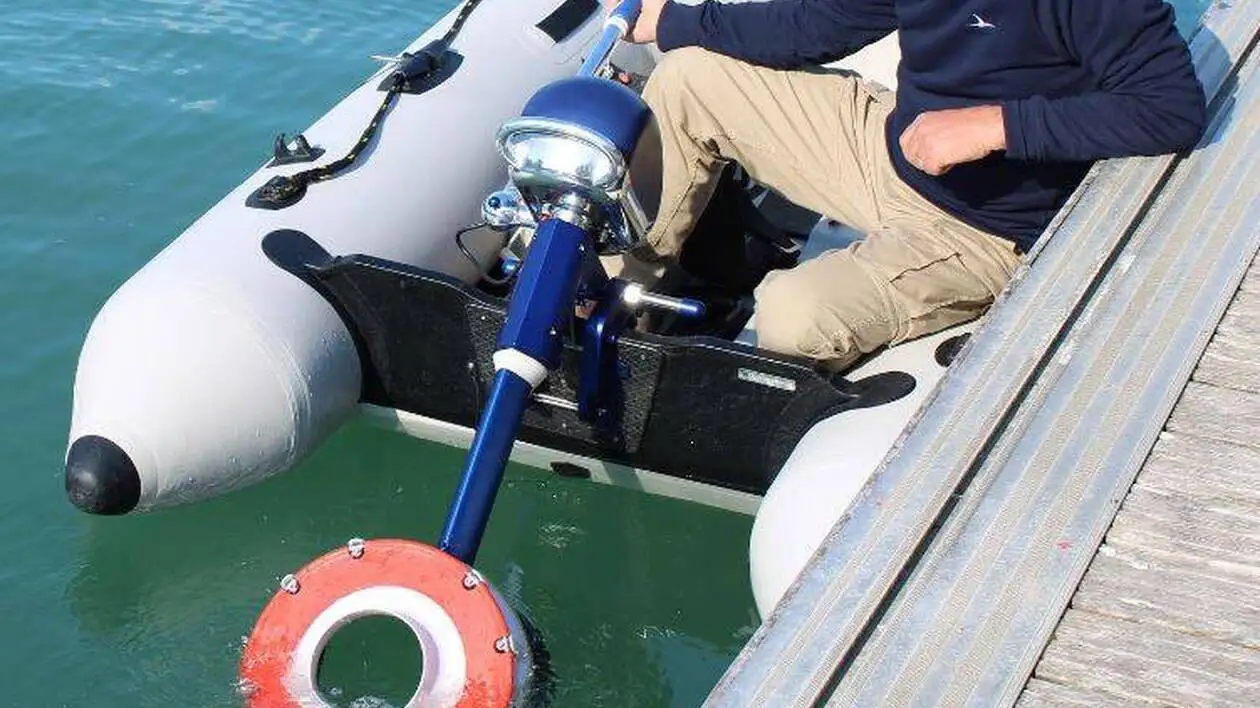
- Navigation innovations: companies like Finx are developing propellerless boat engines that emulate the swimming movements of marine animals, such as dolphins.


Agriculture and energy: key areas for biomimicry
- Agricultural innovations: by studying how bees pollinate plants, we can develop improved agricultural practices and technologies that enhance crop yields.
- Sustainable waste management: the natural processes of decomposition and nutrient cycling inspire technologies for sustainable waste management and recycling.
- Energy efficiency in wind turbines: a novel type of wind turbine that incorporates the grooved design found on humpback whale flippers provides significant energy savings. This innovative application marks a major advancement in the wind energy sector.
Lastly, in the realm of computer modeling, noteworthy developments include:
- Algorithms: the concept of ‘swarm intelligence,’ seen in the behavior of ants, bees, and other social insects, has informed the creation of optimization algorithms in computer science.
- Neural networks: the structure and functionality of the human brain inspire artificial neural networks in AI, enhancing machine learning and problem-solving capabilities.

Notable initiatives by major corporations include:
- Renault Group is focusing on enhancing resource efficiency in hybrid vehicle engines, drawing inspiration from the human body’s metabolism.
- SUEZ is advancing a water filtration system modeled after natural wetlands. This system is designed to offer additional treatments against micropollutants and prevent their spread in aquatic ecosystems, while also supporting biodiversity. It involves a series of water basins populated with diverse, carefully selected fauna and flora that help absorb pollutants like drug residues, solvents, and pesticides.
- Airbus is exploring ways to optimize the mass-to-resistance ratio using algorithms derived from the structures of bones and plants, aimed at improving 3D printing techniques. This approach could substantially lower kerosene consumption in aircraft.
- ENGIE and Polymaris Biotechnology are collaborating to utilize a biopolymer produced from marine bacteria to prevent buildup in cooling systems and industrial piping, offering a non-toxic alternative to harmful chemicals such as chlorine typically used in industrial water processes.
This list is far from complete. For more information on biomimicry, please explore the Biomimexpo page and consider attending the event.
To wrap up, I’d like to echo the thoughts of Alain Renaudin, founder of Biomimexpo:
Biomimicry not only highlights the scientific and technological benefits of drawing inspiration from nature, but it also underscores the political, strategic, and industrial significance of this approach. It serves as a proposal for reconnecting humanity with nature, a novel way to raise awareness about biodiversity, and a chance for France to lead on climate and environmental matters.
Thanks for reading! Kickmaker is a design and industrialization agency for high-tech products. In fact, we help biomimicry companies turn their innovations into reality.


